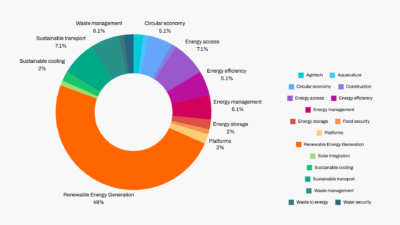
Pakistan is experiencing a solar boom unlike any other. In just the first half of 2024, the country imported over 13 GW of solar panels – more than the total installed capacity of some entire countries (The Great Solar Rush in Pakistan, 2024). This unprecedented growth could push it ahead of its 2030 renewable energy targets years in advance.
The impact is already rippling through communities: farmers are swapping diesel pumps for solar-powered tubewells, industries are securing their own reliable power, and families are reducing their reliance on an overstretched grid. Clean energy is reshaping daily life, and climate entrepreneurship is multiplying its benefits across the country.
From waste-to-energy ventures in Karachi to e-mobility startups in Lahore, Pakistan’s climate innovators are finding practical solutions to real problems. But without stronger support systems, many promising ideas struggle to scale.
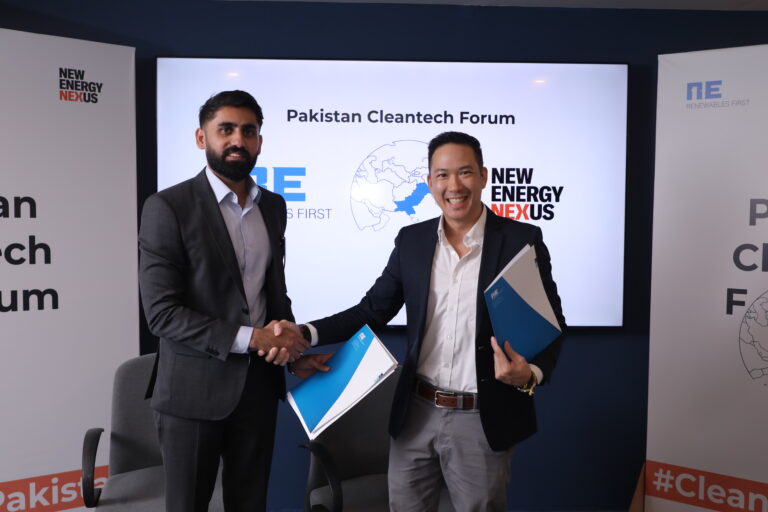

From left: Zeeshan Ashfaq, CEO of Renewables First, and Stanley Ng, Global Partnerships Director at New Energy Nexus
That’s why New Energy Nexus has partnered with Renewables First to launch Climate Innovation Pakistan (CLIP): a national platform designed to empower entrepreneurs, develop a skilled workforce, and shape policies that unlock clean energy innovation for the long run.
Through CLIP, we’re building the kind of ecosystem that helps climate entrepreneurs move from idea to impact:
- CLIP Incubator – Turning early-stage ideas into market-ready solutions.
- New Energy Academy – Training the solar workforce powering Pakistan’s transition.
- ThinkLab – Publishing actionable insights on what’s working or not in Pakistan’s climate innovation landscape, informing smarter policy and investment decisions.
CLIP Incubator: From idea to traction
Inside the CLIP Incubator, founders spend 12 weeks transforming their vision into traction. The program helps them validate products, test solutions with real customers, and refine their go-to-market strategies.
With guidance from mentors who have built and scaled in challenging markets, startups gain not only technical advice but also access to pilots, partnerships, and investors across Pakistan’s growing climate ecosystem.
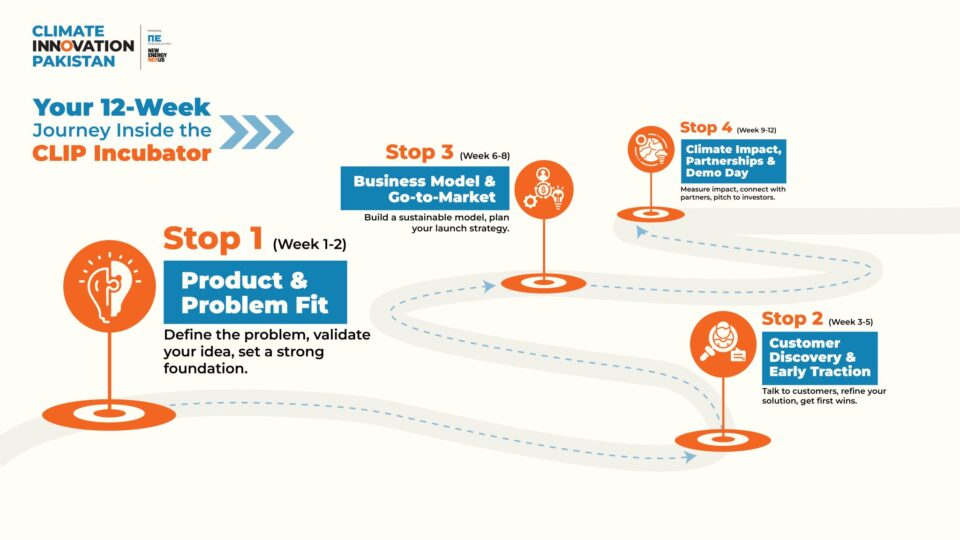
The Clip Incubator journey. Photo from Climate Innovation Pakistan
This is a space designed for entrepreneurs who want to move faster, smarter, and stronger – without giving up equity, and with support tailored to Pakistan’s realities. Learn more and apply here.
New Energy Academy: Building the solar workforce
Pakistan’s solar boom cannot succeed without skilled workers ready to deliver it. That’s why CLIP is launching the New Energy Academy: Solar Fundamentals Training in Islamabad this September.
Developed by New Energy Nexus, GSES Global Sustainable Energy Solutions, and OpenSolar, and implemented in collaboration with Renewables First and the Pakistan Solar Association, the program blends online and in-person learning to train young people for jobs in installation and maintenance. Participants will gain hands-on skills, mentorship, and connections with employers in a sector that’s growing faster than ever.
By preparing the next generation of solar professionals, the Academy ensures Pakistan’s clean energy transition is powered by people as well as panels. Find out more and sign up by August 22.
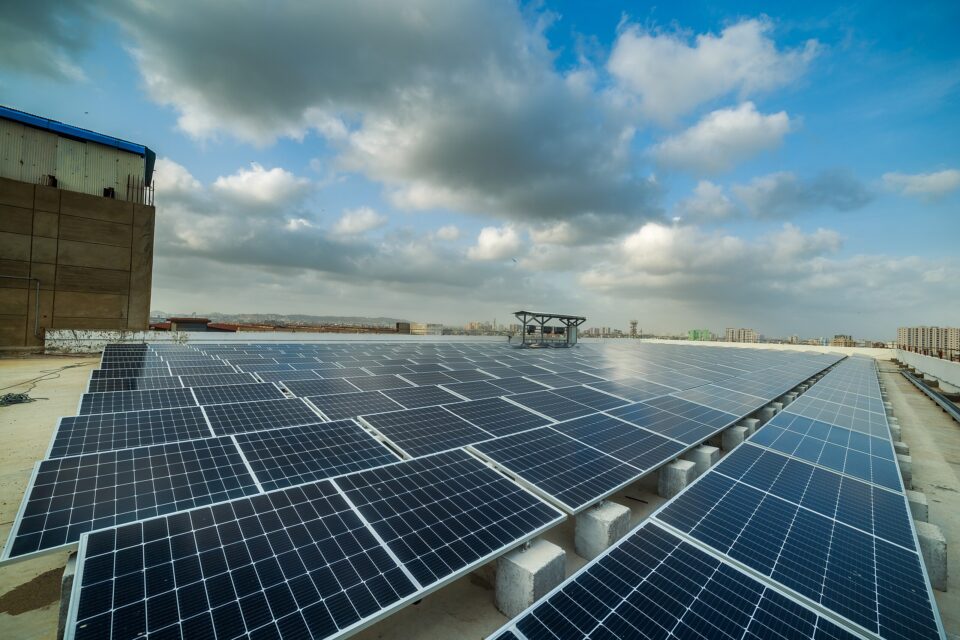

A solar installation in Karachi, Pakistan. Photo from Wikimedia Commons, User: Crosji
Breaking down barriers
Pakistan is one of the world’s most populous countries and one of the most climate-vulnerable. At the same time, it holds enormous potential for clean energy to drive inclusive growth. Yet for many entrepreneurs, barriers to progress persist: limited financing, scarce data, and policy barriers.
CLIP aims to change that. By combining New Energy Nexus’s global expertise in building startup ecosystems with Renewables First’s deep local insights, the platform will help unlock new opportunities for entrepreneurs, investors, and communities alike.
At New Energy Nexus, we support diverse climate entrepreneurs worldwide, giving them the accelerators, funding, skills, and connections to thrive. Through CLIP, we’re expanding that mission in Pakistan, helping climate tech founders transform a historic solar rush into long-term impact for communities and industries across the country.
The path is clear: Build on this clean energy growth in Pakistan and carry it over to the rest of the world. Now it’s time to give innovators worldwide the tools to carry it further.
Ready to scale your own innovation? Check out our programs here.



















![3ge first winner of nex's indonesia [re]power energy policy hackathon 00](https://www.newenergynexus.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/3GE-first-winner-of-NEXs-Indonesia-REPower-Energy-Policy-Hackathon-00-400x267.jpg)