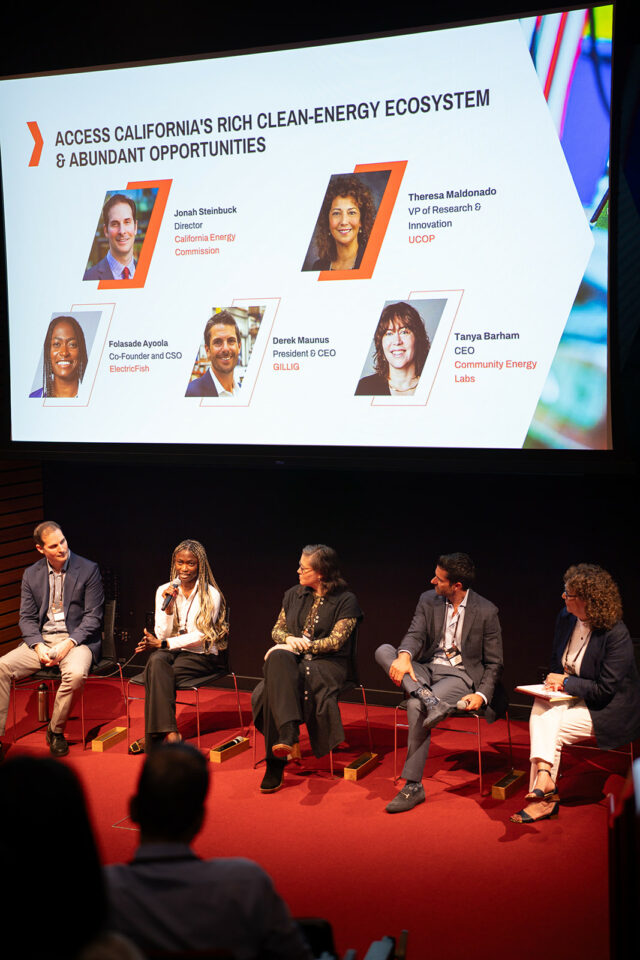
85 cross-sector leaders driving clean energy innovation convene around exciting opportunities, daunting challenges, and innovative solutions from the Golden State and beyond.
In late January, 85 policymakers, industry leaders, labor organizers, nonprofit representatives, and government officials gathered under the shadow of the Golden Gate Bridge for a candid discussion of the opportunities and challenges facing the clean energy industry in our state.
California is in an exciting place to be working in clean energy:
- In 2024, 54% of CA’s electricity is renewable or emits no greenhouse gases, compared to 40% for the US. (Source)
- California had 100 days in 2024 with 100% carbon-free, renewable electricity for at least a part of each day. Thanks to new clean energy resources and the surge in battery storage, the state’s power grid withstood July’s record two-week heat wave – and even exported power to other states. (Source)
- At 10,379 megawatts, the state has increased battery capacity by 1,250% – up from 770 MW in 2019. (Source)
“There’s a whole lot of potential to use the industrial policy instincts to continue to move the ball, but it will need different vocabulary than traditional climate policy advocates have used in the past,” one leader explained about the changing nature of policy in Washington.
Candid comments and bold calls to action are common at the Clean Energy Business Roundtable because the convening operates under Chatham House rules to encourage open, high-trust conversations. This is why no one is directly quoted in this article. New Energy Nexus hosts the annual event to create connections and generate ideas between the top minds in California’s clean energy ecosystem.
The scale and urgency of the challenges facing clean energy in California weighed on the gathering. With the fires in Los Angeles and Washington DC’s rapidly changing political climate, the future looks uncertain and daunting, yet there’s an opportunity to collaborate strategically.
There was a sense of optimism as leaders pressed the importance of the clean energy industry, showing up with authority and empathy and leading the energy conversation.
“We have to make sure we are leading with our heart.”
What would that look like? Here are some of the opportunities and solutions discussed during the event
Tackling the affordability crisis through cutting red tape

Industry leaders continuously lamented California’s onerous and complex permitting process. Battery manufacturers are innovating in California’s universities and labs, harvesting lithium from California’s underground brine (the largest reserve in the nation) and taking those components overseas to be assembled into batteries only to be shipped back. Startups lack the capital and wiggle room to build big facilities, and larger companies don’t see California as a profitable place to do big industry. There was a consistent drumbeat of pleas from industry and labor leaders to the legislators in the room to address this issue.
“Energy is for people in our society. It’s about avoiding rolling blackouts. It shouldn’t be a policy innovation exercise or market optimization.”
One leader pitched the idea of forming county-level teams of experts to help companies navigate regulation since many lack in-house expertise, helping California attract and retain clean energy companies and becoming more attractive than surrounding states or overseas markets.
Beefing up grid resilience and safety

In the wake of the devastating fires in Los Angeles, balancing grid safety with community needs was top of mind. Utility representatives toted advancements in vegetation management and powerline monitoring using drones and AI. Despite all these improvements, representatives and ratepayers voiced frustrations over the prolonged and frequent power safety shut-offs while costs continue to rise.
Leaders suggested undergrounding power lines as a costly but reasonable solution when strategically deployed. There was an example of a utility providing ratepayers in vulnerable areas with generators to help during the safety shut-offs. Microgrids are another solution to help rural customers become more power resilient.
“Utilities are in an impossible situation. It hasn’t rained in Southern California in nine months… We have to be willing to say that if you live in different places, it’s a different reliability framework.”
Last month, The United States Department of Energy announced a $15 billion loan to Pacific Gas and Electric to expand hydropower, improve distribution, increase battery storage, and set up virtual power plants. This move was generally lauded across the gathering as a massive win for ratepayers, who will get improved services and save thousands of dollars in interest over the life of the loan.
Streamlining the fragmented EV charging infrastructure

Most attendees agreed the current state of EV charging in California is a significant barrier to driving further EV adoption and avoiding a plateau. Attendees shared stories of banks of broken chargers, poorly lit stations, too many apps, and terrible or non-existent customer service. Additionally, there’s not enough investment going to simple solutions, like freeway signs pointing to chargers like we do for gas stations.
“If you’re looking for something transformational with limited funds, we have a strong fast charger backbone, which is where we should focus. With our limited time to combat climate change, we need a reliable public network.”
A big light-bulb moment came when a leader pointed out that charging companies don’t think of the end-user as their primary customer. They’re focused on the agencies giving them grant money and the site owners housing the units. There’s no motivation to think about the customer experience piece. It’s just not part of the current business model. That could change as big retailers, like Walmart, get into the charging space and build networks located at their stores.
Building big in California

Growing a clean energy business in the Golden State presents risks and rewards, including access to critical minerals. The Imperial Valley boasts the richest lithium reserves in the nation, making it a prime location for battery manufacturing. Labor groups are urging policymakers to develop in this region to create high-quality jobs in an often-overlooked community.
“This is an opportunity to not just help the residents of Imperial, but all of California.”
Despite these advantages, many battery manufacturers are looking to neighboring Nevada, where permitting is faster and the tax burden less. These factors are critical considerations for California lawmakers as they work to retain manufacturers. One proposed solution is to complete California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA) reviews in advance, reducing permitting delays and expediting projects.
Manufacturing forgoing the California opportunity has a significant impact on the California workforce. Experts emphasized that labor and community benefits must be at the forefront of industrial policy to accelerate the energy transition and strengthen the economy. This means pushing for policies like a decreased tax burden on tools and infrastructures and a more streamlined permitting process.
“The key here is to shift our thinking around labor and community partnerships—not as barriers to growth, but as catalysts for progress. But it requires commitment.”
Banding together and doubling down to continue momentum

One of the main benefits of this gathering was getting everyone in the same room to share experiences, expertise, resources, and ideas. Everyone agreed California sets the pace for the energy transition, and we must work together to get the job done. Clean energy leaders pointed to the immense opportunity for the industry to take a more significant role in garnering support from government officials and investing strategically in crafting more effective policies.
Oil and gas spent $110M lobbying government officials in 2024 [source], compared to $46M spent by renewable energy groups [source]. If the clean energy industry wants to keep up the momentum we’ve gained over the past 10 years, we’ll need to come together and double down on our investments.
“Politics is very much like surfing. In surfing, you cannot manufacture the wave. If you’re on the beach looking at the wave, you’re not riding the wave. Clean energy is standing on the beach.
Why do we have subsidy after subsidy for oil and gas? It’s not magic. It’s politics.”
Wrapping it up
California’s transition to a green industrial economy presents both challenges and opportunities.
By addressing affordability, reliability, and equity concerns, California can continue to serve as a model for a sustainable future if leaders collaborate and prevent politics from interfering with incremental change.
Ultimately, it will take everyone working on the problems from all fronts to usher in a just energy transition. This gathering showed the power and promise of getting the best minds together to work on solutions – this next year will show if the clean energy industry can make good on those promises.
Subscribe to our California chapter newsletter for more clean energy insights and opportunities.