As Pakistan’s climate tech boom accelerates, entrepreneurship is pushing it even further. Founders across the country are turning real community challenges into practical climate tech and resilience solutions.
Their work follows a historic market shift: in the first half of 2024, Pakistan imported over 13 GW of solar panels, a surge that could bring the country ahead of its 2030 renewable energy targets (The Great Solar Rush in Pakistan, 2024). But scaling this transition will require more than panels; it demands innovators who can tailor technologies to local needs.
That’s why New Energy Nexus and Renewables First launched Climate Innovation Pakistan (CLIP): a national platform designed to support climate tech founders, build a skilled clean energy workforce, and strengthen the policies that unlock long-term impact.
“Pakistan’s startup ecosystem must urgently propel the climate tech vertical, as the need for locally developed solutions has never been more critical,” said Zeeshan Ashfaq, CEO of Renewables First. “Through our collaboration with New Energy Nexus, we aim to demonstrate that with appropriate support, investing in climate tech is both essential and economically viable.”
CLIP’s mission is clear – equip founders with the tools to shape a cleaner, more resilient economy, and ensure Pakistan’s climate tech momentum becomes a long-term engine for growth. And it starts with the first-ever CLIP Incubator.
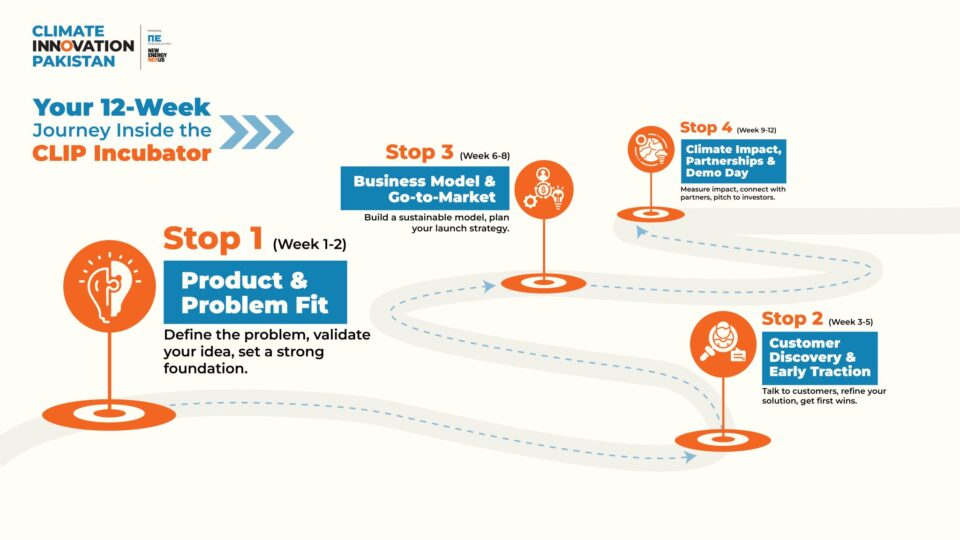
The Clip Incubator journey. Image from Climate Innovation Pakistan
Why the CLIP Incubator Matters
The Incubator is a 12-week, equity-free program helping entrepreneurs validate products, run pilots, refine business models, and connect with investors and partners across Pakistan. It’s built for startups working in the country’s realities, where infrastructure, affordability, and community impact matter as much as technical performance.
“Pakistan is the world’s fifth most populous nation, with its largest industries in high carbon-emitting sectors… Here lies an immense opportunity to ignite the development of groundbreaking climate tech innovations,” said Stanley Ng, Global Partnerships Director of New Energy Nexus.

The CLIP Incubator’s first-ever cohort.
These 11 startups comprise the Incubator’s inaugural cohort, representing the ambition and ingenuity behind the country’s climate innovation wave. Meet them below.
Nimbus Labs
The Problem
Pakistan faces severe gaps in weather monitoring and forecasting. Extreme events disrupt lives and livelihoods, but limited infrastructure prevents accurate early warnings.
The Solution
Nimbus Labs deploys AI and IoT-driven weather stations and machine learning models, powered by low-cost sensor networks, to deliver hyper-local precipitation nowcasts and medium-range forecasts. Their systems strengthen climate resilience and support data-driven decision-making for agriculture, cities, and disaster response.
The Founder
Sarwan Shah is an electrical engineer specializing in Embedded Systems and Machine Learning. His experiences – from founding the Karachi Water Project to Fulbright research and award-winning embedded systems – led him to start Nimbus Labs, aiming to improve Pakistan’s weather monitoring and forecasting infrastructure.
Power Sodium
The Problem
Energy storage in Pakistan remains dependent on expensive lithium imports or polluting diesel generators.
The Solution
Power Sodium builds next-generation sodium-ion and sodium–lithium hybrid batteries with long cycle life and ultra-fast charging, providing clean and reliable power for telecom towers, microgrids, data centers, and renewable energy systems.
The Founder
Ahmad Ghauri brings expertise in aerospace engineering, R&D, and clean energy project management. He co-founded Power Sodium to develop sustainable, locally-manufactured sodium-ion and hybrid batteries that reduce reliance on imported or polluting energy storage systems.
PakPlug’s app interface. Screenshots from PakPlug
PakPlug
The Problem
EV adoption is constrained by a severe shortage of public chargers, despite thousands of unused private chargers across cities.
The Solution
PakPlug allows homeowners to list chargers, while EV drivers book and pay through the app. Their QR-enabled smart switch ensures secure access, accurate metering, and reliable payments — unlocking affordable charging where it’s needed.
The Founder
Roha Rehan, an Electrical Engineering graduate from LUMS, founded PakPlug to make EV charging accessible and community-driven. Her team leverages technical and strategic expertise to connect private chargers with EV users across Pakistan.

Nayab Raza, Founder of Algaverse. Photo from Algaverse
Algaverse
The Problem
Farmers depend heavily on chemical fertilizers that degrade soil, raise input costs, and worsen emissions.
The Solution
Algaverse’s bio-fertilizers offer a climate-resilient, lower-cost alternative aligned with global soil restoration goals, helping farmers improve yields while reducing synthetic fertilizer use.
The Founder
Nayab Raza, a PhD candidate in Environmental Biology at the University of Manchester, founded Algaverse to develop CO₂-capturing bio-fertilizers. Her goal is to provide farmers with sustainable, low-emission alternatives that improve soil health and reduce dependence on chemicals.
SustainAgro by Verdora Ventures
The Problem
Pakistan faces water scarcity, pesticide overuse, and reliance on imported produce.
The Solution
Verdora’s modular greenhouses use climate-smart irrigation that cuts water use by 90%, reduces pesticides, increases yields, and localizes production of crops like cherry tomatoes. This lowers the costs for consumers and businesses.
The Founders
Syed Mahd has over a decade of experience in strategy, investments, and project management. At SustainAgro by Verdora Ventures, he works closely with Asad Shamsi, a finance and strategy professional with expertise in research, consulting, and FMCG. Together, they are integrating climate-smart agriculture practices to improve sustainability and productivity in Pakistan’s horticulture sector.
Pani Express
The Problem
Unreliable municipal supply forces cities to rely on informal tanker operators, which results in waste, high emissions, and inconsistent pricing.
The Solution
Pani Express uses mobile ordering, IoT water-level sensors, and optimized tanker routing to reduce water waste, improve reliability, and provide fair pricing – all while lowering emissions and supporting local livelihoods.
The Founder
Ali Yar draws on years of operational, finance, and HR experience in startups to build Pani Express, a smart water logistics platform. His mission is to make urban water delivery reliable, efficient, and climate-conscious.

Moiz Bhatti presents at an investor summit. Photo from Moiz Bhatti via LinkedIn
EPO (Environmental Productivity Organization)
The Problem
Water scarcity and rising energy costs threaten agricultural productivity in Pakistan.
The Solution
EPO’s closed-loop farming systems use renewable energy and recycled water to produce consistent, high-quality crops while reducing water and energy consumption, offering a resilient solution in water-stressed regions.
The Founder
Moiz Bhatti, an environmental advocate and founder of National Incubation Center Islamabad, co-leads EPO with a team of environmental scientists. They focus on AI-driven solutions for efficient, sustainable urban and agricultural productivity.
MycieBlue
The Problem
Plastic pollution is growing, and sustainable alternatives are either costly or hard to access.
The Solution
MycieBlue produces compostable, lightweight materials using mycelium grown from organic waste, offering low-carbon solutions for packaging and future construction applications.
The Founders
Yumna Ali, an architect and environmentalist, is advancing regenerative biomaterials through mycelium, turning waste into nature-inspired products. She partners with Ameerah Rizwan, a product and interaction designer who brings user-centered design and community insight. The architect–designer pair is pioneering mycelium-based materials and accessible bio-design research in Pakistan.
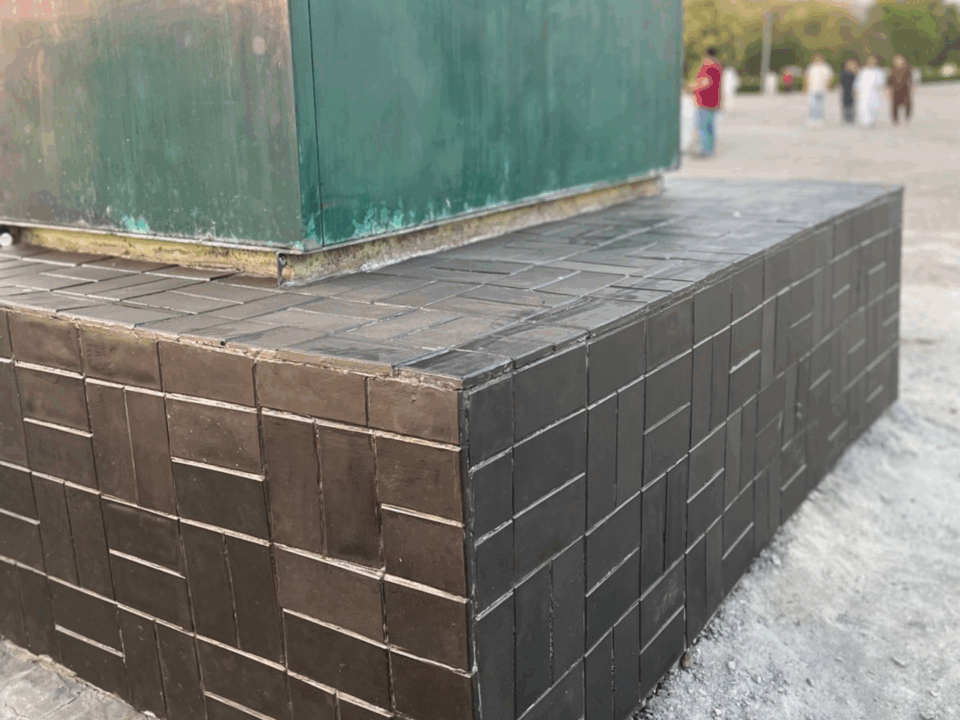

Commercial deployment of 500 Ecobricks Eco-Tiles at F9 Park, Islamabad. Photo from Ecobricks
Ecobricks
The Problem
Millions of tons of plastic end up in landfills or incinerators due to a lack of recycling infrastructure.
The Solution
Ecobricks transforms hard-to-recycle plastics into construction materials supported by AI quality control, reducing waste and enabling circular construction practices.
The Founder
Kashaf Akhtar leads Ecobricks, a team with deep expertise in engineering, AI, and business development. Their focus is on converting difficult-to-recycle plastics into durable, environmentally-friendly building materials.

Screengrab from the Greenova8 website
Greenova8
The Problem
Only large investors typically fund solar and wind projects, leaving everyday citizens out.
The Solution
Greenova8 tokenizes renewable projects, allowing small-ticket investments with real-time tracking. Smart contracts automate payouts, while carbon credit monetization strengthens returns.
The Founder
Ibrahim Afridi started Greenova8 to democratize renewable energy investment using blockchain. He aims to give everyday citizens access to solar and wind projects through fractional ownership.
Recycle Bin
The Problem
Mixed waste contaminates recyclables and sends valuable materials to landfills.
The Solution
Recycle Bin offers digital door-to-door collection with a rewards system, sending materials to verified processors, reducing landfill use and emissions.
The Founder
Adeela Ali, a pharmacist turned entrepreneur, founded Recycle Bin to solve local waste management challenges through technology. She applies her scientific and analytical skills to create scalable, sustainable solutions.

From left: Zeeshan Ashfaq, CEO of Renewables First, and Stanley Ng, Global Partnerships Director at New Energy Nexus
Building Pakistan’s climate future, and taking it global
The founders joining the first CLIP Cohort reflect Pakistan’s growing role in the clean energy transition, and the power of local innovation to reshape a national drive toward a more sustainable future.
This is exactly the kind of work we’re supporting at New Energy Nexus. We’ve backed more than 10,000 clean energy entrepreneurs worldwide. Through CLIP, we’re expanding this mission in Pakistan: helping founders scale solutions, build resilient businesses, and contribute to a cleaner, more inclusive economy.
Pakistan is having a historic climate and clean energy moment. Now it’s time to turn this momentum into long-term transformation, powered by entrepreneurs who understand Pakistan’s needs and are ready to build solutions the world can learn from.
Ready to scale your innovation in Pakistan and beyond? Visit climateinnovate.pk for more climate tech opportunities and updates.




