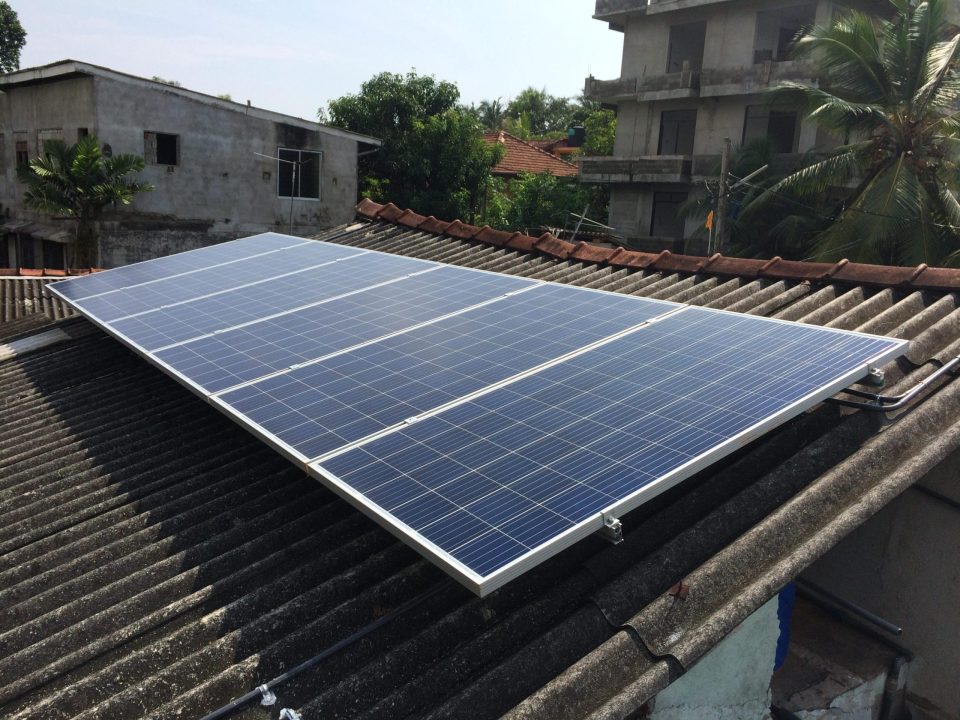
Rooftop solar panel. Stock photo
A recent study by Ateneo de Manila University, published in Challenges in Sustainability, sheds light on the persistent barriers preventing the widespread adoption of rooftop solar power (RTSP) in Metro Manila and nearby provinces. Led by Professor Rosalina Palanca-Tan, the study surveyed 403 respondents to understand why households remain hesitant to invest in solar technology despite its clear economic and environmental benefits.
The study’s findings were recently featured in the Philippine Daily Inquirer, sparking a public discussion on its Facebook post, which highlighted several recurring concerns: high upfront costs, lengthy return on investment (ROI) periods, bureaucratic hurdles, technical challenges, and a lack of government support. Let’s look into the key challenges raised around rooftop solar adoption, and explore potential solutions.
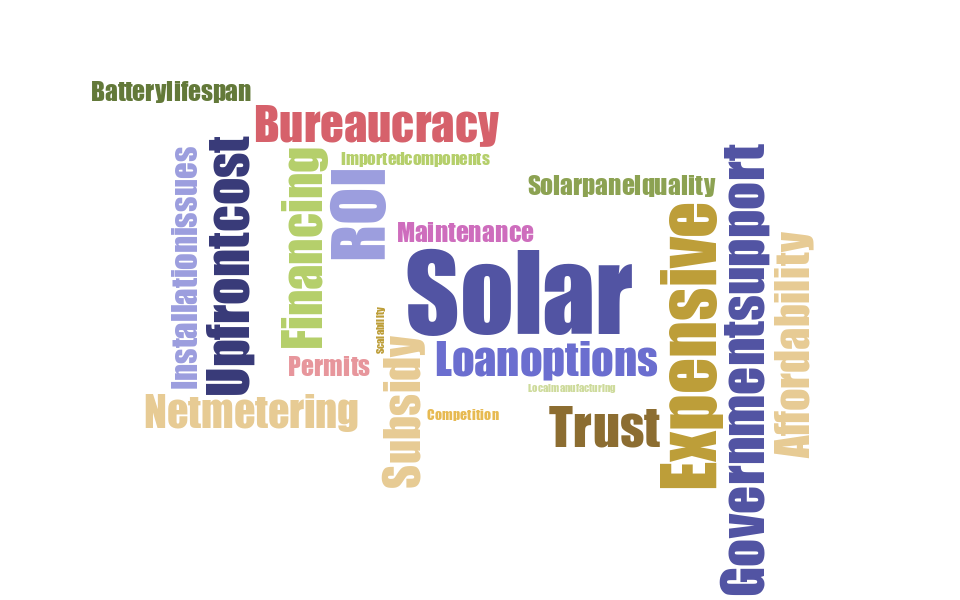
A word cloud generated from people’s responses on the Facebook post.
Why aren’t more Filipinos switching to solar?
1. High cost of installation and ROI concerns
Many consumers cited the high initial cost of installing solar power systems as a major barrier. The upfront investment often matches several years’ worth of electricity bills, making it difficult for households to justify the expense. Additionally, long return-on-investment (ROI) periods discourage adoption, particularly in the absence of accessible financing options.
2. Lack of financing options
Access to financing remains a significant barrier to rooftop solar adoption. With limited options for low-interest loans or flexible payment schemes, households struggle to afford the initial investment, making solar installations less accessible to the broader public, especially to residential consumers.
3. Regulatory and bureaucratic hurdles
The slow and complex application process for net metering was another major concern. Many consumers reported waiting over six months and encountering excessive requirements that hindered their ability to connect their solar systems to the grid.
4. Service and maintenance issues
Some consumers highlighted issues related to improper system sizing, inefficiency, and high maintenance costs. Concerns included roof leaks due to poor installation, the lifespan of batteries, and the disposal of solar panels. These barriers make the transition to solar more challenging for prospective users.
5. Quality of solar technologies & local manufacturing
The absence of local solar manufacturers results in reliance on expensive imported components. Concerns about substandard or inefficient technologies make consumers hesitant to invest.
6. Lack of government support and incentives
Unlike countries such as Australia and Canada, which offer tax breaks, subsidies, and no-interest loans, the Philippine government provides minimal financial incentives for residential RTSP. This lack of support further discourages households from making the switch to solar energy.
7. Limited competition in the market
The industry is still dominated by a few major players, limiting consumer choices and competitive pricing. More players entering the market could drive innovation and lower costs through competition.
Who’s addressing these gaps?
At New Energy Nexus Philippines, we recognize that overcoming these barriers requires a multi-faceted approach—one that not only enhances technical expertise but also builds trust within communities. This is why it’s important to empower the solar industry, especially smaller players, with the right tools and knowledge to drive solutions forward. Our programs, particularly the Solar Innovation Program (SIP) and Solar Community Meetups, are designed to do just that.
Strengthening the Solar Industry
SIP provides targeted support for solar PV installers, engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) companies, and solar equipment suppliers to improve their competitiveness in the market. Through learning sessions and workshops, participants gain essential knowledge in:
- Addressing common challenges in closing deals with clients;
- Effectively promoting and marketing their services;
- Exploring financing mechanisms with financial institutions to make solar more affordable for households; and;
- Expanding business opportunities beyond residential installations.
By empowering solar entrepreneurs, SIP tackles concerns related to business growth, financing gaps, and limited competition in the market. A stronger and more competitive solar industry ultimately leads to better installation quality, reduced costs, and more accessible financing options for households.

SIP 2024 graduates during the culminating activity in Cebu City.
Building Trust in the Industry
Beyond technical training, shifting public perception is crucial for accelerating RTSP adoption. Our Solar Community Meetups serve as a bridge between solar entrepreneurs, technical experts, policymakers, and consumers by fostering collaboration and knowledge-sharing. These gatherings provide a space for entrepreneurs to exchange insights and share best practices, address bureaucratic challenges with government stakeholders, streamline net metering processes, and advocate for stronger policy support. Additionally, they highlight success stories from early adopters, encouraging more households to consider solar power.
By fostering an ecosystem of collaboration and trust, Solar Community Meetups contribute to addressing skepticism and misinformation surrounding RTSP. The insights gathered from these discussions also help inform future policy recommendations, ensuring that the needs of solar entrepreneurs and consumers are effectively addressed.

DOE Assistant Secretary Mylene Capongcol presenting the Department of Energy’s renewable energy plans at the SCM in Davao.
A collective effort for solar growth
The concerns raised in the Facebook post reflect the frustrations and aspirations of many Filipinos when it comes to solar energy adoption. While challenges such as high costs, bureaucratic red tape, and technical difficulties persist, programs like the SIP and Solar Community Meetups provide platforms that empower solar entrepreneurs to drive industry-wide improvements.
Panel discussion during the SIP 2024 culmination featuring Hon. Nestor Archival (Cebu City Government), Engr. Titus Ragrario (Jinko Solar), Engr. Richard Alfafara (Visayan Electric Company – VECO), and Engr. Woodrow Pino (Woodrow Solar Power), sharing insights on accelerating rooftop solar adoption. Photo
Ultimately, expanding the adoption of RTSP in the Philippines requires a collective effort from businesses, the government, private companies, and Filipino communities. By equipping solar entrepreneurs with knowledge and resources, and by fostering trust through community engagement, we can create a more inclusive and resilient solar industry that benefits both consumers and the environment.
Want to get more involved in the Filipino clean energy space? Learn more about our programs in the Philippines here.